Key Takeaways
- The mathematical formulas and computational processes by which Google’s search engine determines the relevance and order of web pages in the results for a query is referred to as its algorithm.
- Google has a long history of algorithm updates designed to bring users information and content that they find helpful, accurate, and engaging, with the most recent being in the latter half of 2022
- These algorithm updates generally seek to weed out ‘thin’, unhelpful content, as well as what it denotes as spam.
- Staying ahead of these updates and knowing what the expect help will help websites and brands hang onto their visibility.
The SEO landscape has evolved significantly over the last decade, and the main reason for this is the constant updates to search engine algorithms. The leading search engine, Google, has made several significant updates to its algorithm in order to provide users with the best possible results. These updates have had a considerable impact on SEO best practices. This blog lists some of the major algorithm updates made by Google and their implications for search and SEO.
If you want to track all of Google’s recent algorithm updates, small and large, they offer an index here: List of Google Search ranking updates.
What are Google algorithms?
Google Algorithms are a set of complex mathematical formulas and computational processes used by the Google search engine to determine the relevance and order of web pages in the search results for a given query. These algorithms provide the most relevant and useful results for a user’s search inquiry by analyzing ranking factors such as keyword relevance, content quality, website performance, and user engagement.
The algorithms consider hundreds of ranking factors or signals, such as the words on websites, the freshness of content, and the number and quality of links pointing to a website. Google updates its algorithms regularly to improve its search results accuracy and relevance and combat web spam.
A timeline of Google’s biggest algorithm updates
In the past, Google would only make a few updates to its algorithms once a year, but today, it makes thousands of changes and tweaks yearly. The majority of these updates are minor and go unnoticed. However, occasionally, Google releases major updates that significantly affect the search engine results pages (SERPs), such as
2022 – Helpful Content Update
The 2022 Helpful Information Update is a tweak to Google’s algorithm that favors content users consider helpful and useful. This improvement emphasizes the quality and relevancy of content rather than just keyword optimization. As a result, websites with in-depth and practical content that meets visitors’ wants and questions are more likely to rank higher in search engine results.
This algorithm update also supports using structured data and other technical SEO best practices to help search engines understand a website’s content. Overall, the Helpful Content Update seeks to enhance the user experience by delivering more relevant and meaningful search results.
If you’ve noticed recent traffic declines to a blog, this may be the cause. Learn how to fix declining blog traffic.
2021 – MUM (Multitask United Model)
Announced by Google at I/O 2021, MUM stands for ‘Multitask United Model,’ a name that alludes to the capability of this new algorithm: it can perform numerous jobs simultaneously. In addition, it can read, understand, and learn in over 75 languages from various sources, including video and audio.
Source: Google Blog
MUM will aggregate information from multiple sources to provide multi-layered solutions to complex search queries. It has already been used in COVID-19 vaccination searches, but that is only the beginning. Google’s MUM AI will be gradually introduced over the next few months and years, so don’t anticipate significant changes to occur suddenly.
2021 – Google May Core Update
This update was released in May 2021 and was designed to improve the overall quality of the search results for users. It focused on various factors, including website relevance, authority, and trustworthiness. As a result, websites that provided high-quality and relevant information improved their search rankings, while low-quality or spammy ones saw a decline.
2021 – Page Experience Update (Core Web Vitals)
This update, launched in May 2021, expands on the Core Web Vitals update by incorporating additional metrics relating to website user experience. It focuses on a variety of variables, such as a webpage’s loading speed, mobile friendliness, website security, and the presence of intrusive adverts. Websites that delivered a high-quality user experience improved in search ranks, whereas others that were slower or less user-friendly fell.
2020 – September Core Update
This upgrade was made available to users in September 2020, and its primary purpose was to enhance the general quality of the search results displayed to them. It concentrated on a variety of aspects, such as the significance, authority, and dependability of websites. As a result, websites that presented high-quality and relevant content saw an improvement in their search ranks, whereas websites that were of low quality or contained spam saw a fall in their rankings.
2020 – Google Core Web Vitals
Google released the Google Core Web Vitals update in May 2020 as a set of metrics to assist website owners in gauging the user experience of their pages, particularly in terms of loading time, interaction, and visual stability. In addition, the update attempts to recognize and highlight web pages that offer quick and effective user experiences across all platforms and devices.
Google’s Core Web Vitals. Source: Google.
The Core Web Vitals include:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which measures loading performance.
- First Input Delay (FID), which measures interactivity.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), which measures visual stability.
Google has announced that in the future, it intends to utilize these measures as ranking signals, which means that a website’s performance on these metrics will be used to decide its search engine ranking. This update is significant for website owners because it provides a clear picture of how their website functions in terms of user experience and what they can do to enhance it.
Learn more about page speed and how it relates to SEO.
2019 – BERT
The October 2019 BERT update used cutting-edge natural language processing methods to comprehend the purpose of a user’s search and deliver more relevant search results. BERT, or “Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers,” is a machine learning model that can recognize the context of words in a phrase. This change made it easier for Google to determine the purpose of a user’s search query, particularly for long-tail and conversational inquiries, and to deliver more pertinent results.
The BERT upgrade was particularly crucial for inquiries that employ natural language and depend on context to determine the purpose of a search. It enables Google to interpret word meanings in the context of the full search and produce more precise search results. Additionally, this upgrade enhanced the search outcomes for voice searches and featured snippets.
Overall, the BERT update helped Google’s search results be more relevant and accurate by better understanding user intent and returning more relevant results, especially for more complicated and conversational inquiries.
2018 – Medic Update
The Medic Update, targeted websites focused on health and wellness, was first seen in August 2018. The update promoted reliable and educational content and demoted low-quality or misleading content in an effort to improve the quality of Google’s search results for medical-related searches.
Most of the websites impacted by this update had poor content, minimal original research, or were disseminating false or misleading information. On the other hand, websites with a solid reputation, valuable content created by subject-matter experts, and such content were more likely to be rewarded with higher search engine ranks. Therefore, this update was crucial for the health sector since it ensured users could receive accurate and trustworthy information about their health and fitness issues.
In general, the Medic update assisted in enhancing the caliber and relevancy of the content that appears in Google’s search results for queries relating to health and wellness, ensuring that the data shown to consumers is correct and reliable.
2018 – Google E-A-T
The Google E-A-T update, which Google revealed in August 2018 as part of its Quality Rater Guidelines, is not a specific algorithm update. Instead, it is a series of recommendations for website quality and content relevancy. Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness are abbreviated as E-A-T. This upgrade stressed the value of excellent material and the standing of the website and its authors.
Google aims to ensure the information displayed in its search results is accurate, trustworthy, and informative and that it originates from reliable sources. As a result, higher search engine rankings are more likely awarded to websites with a solid reputation, helpful and educational information, and are written by subject-matter experts.
This update was intended for websites in the Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) category, which are described as sites that can significantly impact a person’s current or future well-being. Financial advice, health-related content, and legal guidance are a few examples. Overall, the Google E-A-T upgrade aided in improving the quality and relevancy of content appearing in Google’s search results, as well as ensuring that the information presented to users is accurate and trustworthy. As a result, the YMYL categories were tweaked again in the next update.
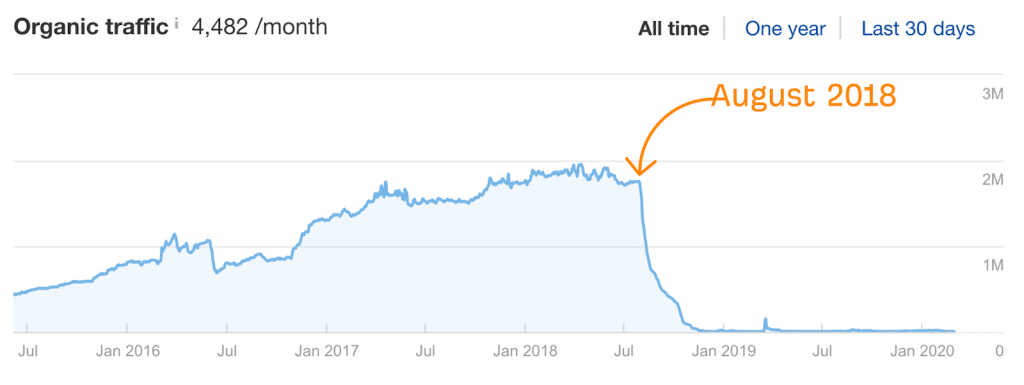
YMYL sites that didn’t already incorporate E-A-T guidelines saw a drop in August of 2018. Source: AhRefs
2018 – (Mobile) Speed Update
The Speed Update, commonly referred to as the “Mobile Speed Update,” was an algorithm update to Google’s search results for mobile devices that were made public in July 2018. The update concentrated on website speed, particularly how quickly pages loaded on mobile devices. Google made it clear that this upgrade only applied to a small portion of inquiries and that each business would have a different standard for what would be considered a sluggish loading page.
In the search results, websites that took too long to load on mobile devices were penalized, while those that loaded quickly experienced an improvement in their search engine ranks. The goal of this upgrade was to enhance the user experience by making it easier for mobile users to find the information they needed more quickly.
2017 – Fred
Released in March 2017, the Fred update is a change to the Google algorithm that targets low-quality content websites that disobey the search engine’s webmaster standards. The upgrade targeted websites that were believed to be breaking Google’s rules, especially those more concerned with making money from ads than giving consumers useful material.
Websites impacted by this update had poor content, a strong emphasis on earning advertising money, and few or no distinctive selling qualities. With this upgrade, Google aimed to reward websites that offered their customers valuable and helpful content while removing low-quality, “thin” content from its search results. Overall, the Fred update raised the caliber of Google’s search results and made it harder for websites to manipulate the search results.
2016 – Possum
Google updated its local search algorithm in September 2016 with the “Possum update.” By using several new elements, such as the searcher’s physical location, the business’s address and phone number, and the authority and relevance of the website, the update sought to increase the relevance and diversity of Google’s local search results.
Additionally, the upgrade gave more weight to a business’s proximity to the searcher, increasing the likelihood that those establishments would appear in search results. It also impacted how Google handled duplicate business listings, which increased the need for accurate and consistent information for firms across all platforms. Overall, the Possum update made it harder for companies to trick the system while increasing the relevancy and diversity of Google’s local search results.
2015 – RankBrain (Hummingbird Update)
The RankBrain upgrade was a major algorithm update published in October 2015 as part of the Hummingbird update. It used machine learning to determine the intent behind a question and then match it with the most relevant search results. The update intended to increase the relevancy and accuracy of Google’s search results by utilizing artificial intelligence to grasp the meaning of search queries better.
RankBrain employs a neural network to process and understand natural language searches, allowing it to better understand the intent behind a user’s search and give more relevant results. This change has enabled Google to handle a broader range of questions, particularly more sophisticated and conversational queries, and better grasp their intent. Overall, RankBrain has improved the accuracy and relevance of Google’s search results, hence improving the user experience.
2015 – Mobile Update (Mobilegeddon)
The Google algorithm upgrade known as “Mobile update,” commonly referred to as “Mobilegeddon,” was made public in April 2015. Giving preference to mobile-friendly websites in Google’s mobile search results was the major goal of this upgrade. This upgrade was important because it changed how Google ranked websites, making mobile-friendliness a crucial component in a website’s search engine ranking.
Mobile-friendly websites witnessed an improvement in search engine rankings, while non-mobile-friendly websites received penalties. This upgrade had a significant role in the continued trend of rising mobile and declining desktop usage, making it possible for mobile users to access the information they require more conveniently.
2014 – HTTPS/SSL
The 2014 HTTPS/SSL update was an algorithm change that attempted to provide websites that employ secure HTTPS/SSL connections a minor ranking boost. The update aimed to persuade website operators to employ secure connections to safeguard user information and advance internet security. The HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) standard encrypts data transferred between a website and a user’s browser, making it far more difficult to intercept or alter that data.
HTTPS is a protocol for secure communication on the internet. HTTPS is the successor to SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). By encouraging website owners to switch from HTTP to HTTPS, Google made it plain that it values website security and that doing so will increase both the safety of the website and its search engine rating.
2014 – Pigeon
Google introduced the Pigeon update in 2014, designed to enhance local search results by boosting the relevancy and accuracy of the search results. For companies relying on Google Maps and Google My Business listings, this update severely impacted local SEO. In addition, the ranking of local directories and review websites was also affected, emphasizing the necessity for businesses to maintain accurate and current information on these systems. The Pigeon upgrade enhanced the user experience by delivering more relevant and practical local search results.
2013 – Hummingbird
Google’s search engine underwent a significant algorithm modification in 2013 called Hummingbird that aimed to enhance how well it understood and processed search requests. By focusing on the intent behind a search question rather than just matching terms, the update hoped to increase the accuracy of search results.
Additionally, Hummingbird improved Google’s comprehension of the semantics and context of the words used in a query. As a result, Google was able to provide longer-tail and conversational search searches with more relevant results. The change also affected how Google treated synonyms, increasing the likelihood of responding to a query even if it were phrased differently.
2012 – Pirate Update
Google’s algorithm update, known as “The Pirate Update,” targeted websites offering pirated content, such as copyrighted movies and music. The upgrade sought to penalize rogue websites while promoting trustworthy, conforming websites. The change was designed to make it harder for users to find pirated content and assist rights holders in better managing and protecting their intellectual property online. The update rolled out as intended, and many sites that offered pirated content suffered a considerable decline in traffic due to the update’s significant impact on their search rankings.
Source: Engadget
It should have been called the Anti-Pirate update.
2012 – Penguin
The 2012 Penguin update was an algorithm change to Google’s search engine ranking system. It targeted websites utilizing unethical methods, such as purchasing links or joining link networks, to raise their search rankings. The upgrade attempted to reward sites that naturally gained connections while discouraging sites that utilized these black hat tactics.
The modification significantly impacted many websites’ search rankings and caused numerous changes to SEO tactics, especially concerning link building. The update was viewed as a continuation of the Panda update because both upgrades sought to raise the overall caliber of search results by removing subpar websites from the top search results.
2012 – Venice Update
In February 2012, Google released an upgrade to the algorithm known as “The Venice update.” The primary objective was to enhance local search results by adding more local search signals to the algorithm. With the upgrade, search queries with a local purpose should return more precise results.
For example, if a user searched for a “suit tailor” in a city, the update would return results for tailors in that same city rather than just suit tailors generally.
By giving local firms the advantage over out-of-town competitors, this modification also helped to increase their visibility in search results. The Venice update’s overall goal was to improve user experience by delivering more accurate and pertinent local search results.
2011 – Panda
Google’s search engine ranking system underwent a significant algorithm modification in 2011 known as the “Panda Update,” which was created to penalize “thin” or low-quality webpages and reward informative, high-quality websites. The upgrade targeted websites with a large percentage of low-quality material, including content farms, duplicate content, and keyword stuffing.
The update aims to increase the general quality of search results by promoting websites with more practical, informative material and removing low-quality sites from the top search rankings. The modification significantly impacted many websites’ search rankings and caused numerous revisions to search engine optimization (SEO) tactics.
Stay ahead of updates with Redefine
It is essential for websites to stay current with Google’s algorithm updates to ensure they maintain their search rankings and provide the best possible experience for users. Year after year, Google is pushing similar best practices and rewards websites that:
- Provide high-quality and relevant content that addresses the needs and interests of your target audience.
- Incorporate keywords and phrases relevant to your industry and regularly update your website with fresh and informative content.
- Optimize website performance by compressing images, minifying code and using a content delivery network (CDN)
- Make sure your website is mobile-friendly
- Implement website security by using HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) to prioritize secure sites and protect website data from hackers.
- Improve user experience and attract more organic traffic and potential customers.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve the user experience on your website and attract more organic traffic and potential customers. It’s essential to stay current with the algorithm updates and adapt your SEO strategies accordingly to ensure your website is always in compliance with the latest guidelines set by Google.
If this is all a little too much to keep up with the ever-changing landscape of SEO and Google’s algorithm, make it easier for yourself by leveraging Redefine’s expert SEO and digital marketing services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you improve your website’s search engine rankings and user experience.