- A 404 error means that the page can’t be found. Usually, this happens when the URL or its content was deleted or moved.
- 404 errors are bad for the user experience and bad for SEO — Google will classify your site as unreliable if it sees that a page that had previously existed is no longer available.
- It’s important for you to conduct regular checks on your website to keep track of any 404 errors.
- You can look for 404s using Google Search Console, Google Analytics, or Google Webmaster Tools.
- Thankfully, fixing 404 errors isn’t rocket science and you don’t have to be a coding expert to implement them.
You’ve spent hours, days, and weeks creating the perfect page for your website. Your ideal client finds it and clicks on the page. Engaged clients, check.
And they come face to face with the dreaded 404 page.
Do you think your potential client or customer will navigate back to your homepage and try again? Or do you think they will get annoyed and go to another website?
Chances are, they will just leave. However, with some basic knowledge and a few simple strategies, you can optimize your website to avoid 404 errors and learn how to best deal with them when they come up.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- What a 404 error is
- Why 404 errors are bad
- The differences between a 404 and a soft 404
- How to identify 404 errors
- How they can be fixed
- Tips for your 404 pages
Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about 404 errors so you can create a website your audience will have no problem navigating.
What is a 404 error?
Many people get stuck on 404 meaning, so let’s start by explaining this concept. A 404 error means that the page can’t be found. Usually, this happens when the URL or its content was deleted or moved.
For example, let’s say you own an e-commerce company and you used to sell blue water bottles but now the supplier has discontinued them. So, you delete the product page but forget to remove the link to the page from the “Bestsellers” section of your website. When a user clicks on the link to the water bottle, the URL will then lead to a page that doesn’t exist, no doubt irritating your customer.
However, 404 errors can also happen for other reasons. For example, they can happen if the URL was typed incorrectly in the browser or was not written correctly when you created the page. It can also happen if there’s a problem with the server or the domain name no longer exists, such as when someone removes their website from the Internet entirely.
Why 404 errors are bad
You don’t want to risk hyping up your customer about a product or service only for them to find out it doesn’t exist. However, 404 errors are bad news for more reasons than just making your customers angry. 404 errors are dangerous because you might not even notice they’re there until you start losing traffic on your site.
Some of the only ways you’ll know if you have a 404 error is if someone lets you know (which is unlikely) or you run into it yourself when navigating or testing your website.
404 errors are also bad for your SEO as Google will classify your site as unreliable if it sees that a page that had previously existed is no longer available. If your sitemap is consistently shown to be inaccurate, you can be sure you won’t be ranking as highly as you used to. Even worse, you’ll lose trust with your visitors as they’ll consider your website to be unprofessional.
Keep in mind that it’s not usually the 404 error page itself that alerts Google that your site is unreliable, but the broken links that lead to the missing page. If you’re rewriting a bunch of pages on your website, be sure to check each internal link so that you’re not accidentally linking to pages that no longer exist on your site.
What is the difference between a 404 and a soft 404?
Most people don’t realize that there are two types of 404s. A soft 404 still shows visitors that a page doesn’t exist (like a regular 404) but returns a 200 status code to the search engine. A 200 status code tells the search engine that the page loaded properly, but it will notice that the content of the page no longer exists.
In other words, soft 404s happen when the content of the page was deleted but the page still exists, while with a regular 404, the page doesn’t exist anymore at all.
Let’s go back to our e-commerce website example. Let’s say you didn’t delete the product page after your blue water bottle supplier discontinued their product. You kept the page but simply deleted what was on the page, like the product description and order button.
Since the page still exists, it would load in a search engine, but the search engine will recognize that there’s nothing on the page and label it as a 404. Soft 404s are especially bad for SEO because if you have more than one, Google will consider these as duplicate pages, which will hurt your SEO ranking.
How to identify 404 errors
The chances that a customer will contact you to let you know that you have a 404 error are slim. This is why it’s important for you to conduct regular checks on your website to keep track of any 404 error causes.
Luckily, free online tools you can use to identify 404 errors. If your site has 500 URLs or less, you can use a site crawler such as Screaming Frog for free to quickly find broken links.
In Screaming Frog, start a site audit and click on “Response Codes” in the top right corner. Click on the Filter icon and select “Client Error (4xx).” Then, Screaming Frog will crawl your website to check for any broken links, but keep in mind that it won’t look for other 404 errors.
To find all the 404 errors on your site, try one of these three ways:
Google Webmaster Tools
Log in to your Google Webmaster Tools account and click on the “Crawl” tab. Click on “Crawl Errors” and you’ll see a list of your site’s pages that Google’s crawlers can’t access. Google will think that these pages should exist because they were either previously included on your sitemap or existed on your website before.
Google Search Console
Log into your Google Search Console Account and go to “Coverage.” Click on the “Excluded” tab on the right side and make sure it turns gray and that the box is ticked. Search Console will then give you a list of all your 404 pages, as well as any soft 404 pages.
Google Analytics UA (now retired)
This method is a little bit more complex, but it gives you the most detail. Log into Google Analytics. On the left side menu, click All Behavior→Site Content→All Pages. Where it says “Primary Dimension,” click on the “Page Title” tab. In the search bar, type in “404” and hit enter. On the left side, underneath “Page Title,” it will tell you which pages are tagged (marked) with a 404. Click on each title to see exactly which URLs are returning a 404 page.
Google Analytics 4
Thankfully this is a rare occasion where things stayed mostly familiar with Google Analytics 4. To find 404 pages and the pages that are linking to them, you can follow these steps:
- Open the Pages and Screen report
- Select Page Title and Screen Class as dimension
- Select Page Path and Screen Class as a secondary dimension
- Go to your website and type in any invalid URL. (Ex: https://www.redefineyourmarketing.com/that’s%20not%20real)
- Read the browser tab for this page to see what your 404 page title is.
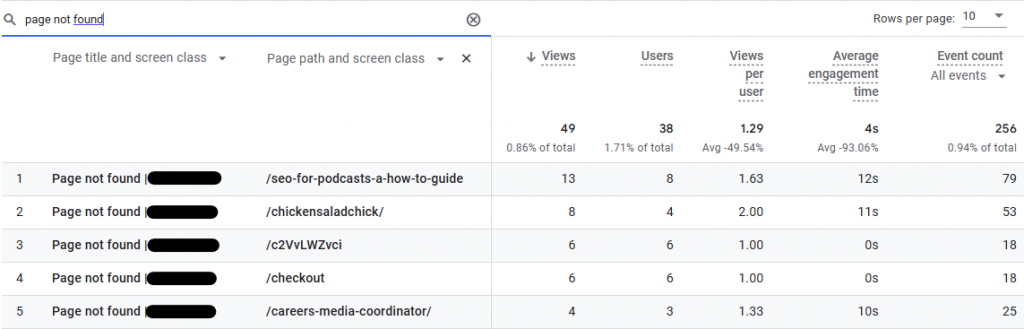
- Back in GA4, you can now search for your 404 page title, and you should see a similar result to the image shown below.
How you can fix 404 errors
Thankfully, fixing 404 errors isn’t rocket science (or computer science?), and you don’t have to be a coding expert to implement them. Before you start, make sure to refresh the page, clear your cookies/browser cache, and check that you typed the URL correctly. Let’s fix that pesky error code!
Fix the source link
If the broken link exists on your website and you have control over fixing it, then go ahead and fix the link.
Going back to our water bottle example (is it getting watered down yet?), let’s say your “Bestsellers” page is the one that has the broken link to the water bottle page that no longer exists. All you need to do is either delete the link or modify the link to go to a different page, such as to another best selling product.
Since most broken links tend to be on pages you can’t directly fix or change, then the other option is to create a redirect.
Create a redirect
A redirect happens when the error page automatically directs the viewer to a different, working page on your website. This way, the user won’t actually see the 404 error page and will instead be redirected to a different page of your website. Just make sure to redirect your viewer to a page that would be useful to them and that’s relevant to what they were actually searching for.
For example, you don’t want to redirect someone looking for a specific pair of running shoes to a page about cars. Redirecting them to a page on other running shoes on your website would be an example of a useful redirect.
Tips for your 404 pages
Since 404 pages are likely inevitable at some point in your website’s (hopefully long) lifetime, it’s a great idea to customize your 404 pages. Since the search engine needs some time to stop showing a 404 error after you’ve fixed it, you need to show your client more than a dead end on your website.
Here are some ideas for customizing your 404 pages:
- Add some humor
- Keep the wording or theme consistent with your brand
- Add a funny and related picture
- Include links to similar pages on your website
Customizing your 404 pages can help keep visitors on your website and help users find what they were initially looking for.
If you have some coding experience, then you can create your own 404 pages, or ask your web designer to make them for you.
Have more questions about 404s? Ask us today!
We hope this article gave you a helpful explanation of 404 errors. You should have a better understanding of how to avoid them and how to fix them if they appear.
404 errors can be annoying, but luckily, there are ways to fix them and to make sure they’re not as jarring to your website visitors.
If you still have questions about 404s, contact our dedicated team of digital marketing specialists so that we can help you make your website even better.